Historically, our energy needs were quite simple and low. Families often needed to power a couple of lightbulbs and maybe a radio. Therefore, the grid system would work in one direction, from the power generation source to the house. There would be no communication between utility company and customer, and no monitoring of energy usage. However, our energy demands have become significantly more complex, which has called for a more developed and advanced smart grid system. What is most special about the smart grid system is that electricity can travel in both directions. While customers still call electricity from the utility company, they also can produce energy and send it to the grid (through solar panel systems or wind turbines).
What makes a smart grid ‘smart’?
What makes a smart grid 'smart'?

What the smart grid also offers is constant communication between the customer and utility company, which allows for the following technologies to take place:
- Variable Pricing
- A common practice is when utility companies offer a changing rate for the electricity you use. Primarily, they charge significantly lower rates for the later hours of the day. This way, the power grid will not be under as much stress during the daytime hours, when most people are home and using their heating, cooling, entertainment, and other systems.
- Demand Response
- Demand Response (better known as DR) is a common way of preventing blackouts and brownouts. Mostly aimed toward commercial (but also residential) customers, utility companies incentivize their customers to use less electricity during moments of high stress on the grid. For example, factories are paid large sums of money to reduce their energy during hot summer days when most homes use their air conditioning. This is all possible due to the smart grid, which allows for constant communication between utility companies and customers.
- Optimization and remote control of devices
- Important components of a smart grid are smart devices. These are devices that can be controlled remotely from cell phones or laptops. This allows one to customize when these devices run, hand in hand with variable pricing or demand response. For example, you can have your washing machine run at night when electricity is cheaper, or shut off devices during a demand response event to gain income from your utility.

Major benefits of having a smart grid
- Less use of fossil fuel power plants
-
- During the months when there is a lot of stress put on the power grid, power plants have to produce more to keep up with the demand. This often comes in the form of carbon-emitting power plants. With demand response and other tools the smart grid offers, we can reduce the energy demand at these peak times, therefore, reducing the need to use more fossil fuel power generation.
- Greener power production
- Enabling people to receive energy from the grid and send energy into the grid creates the possibility of residential power production. You have certainly seen this through solar panels in your neighbourhood or community. These solar panels are sending energy in to the grid, reducing the need for fossil fuel power generation.
Where does electricity come from?
Where does electricity come from?
Electricity plays a huge role in modern societies. Over the years, we have become dependent on using electrical appliances and light.
We all use electricity, but where does it come from?
Electricity always has to be generated in power plants of various sizes from different energy sources, like coal, gas, nuclear, wind, solar, etc.

How is electricity generated?
To help explain how electricity is generated, we can firstly distinguish between the types of power plants:
Energy generation technology:
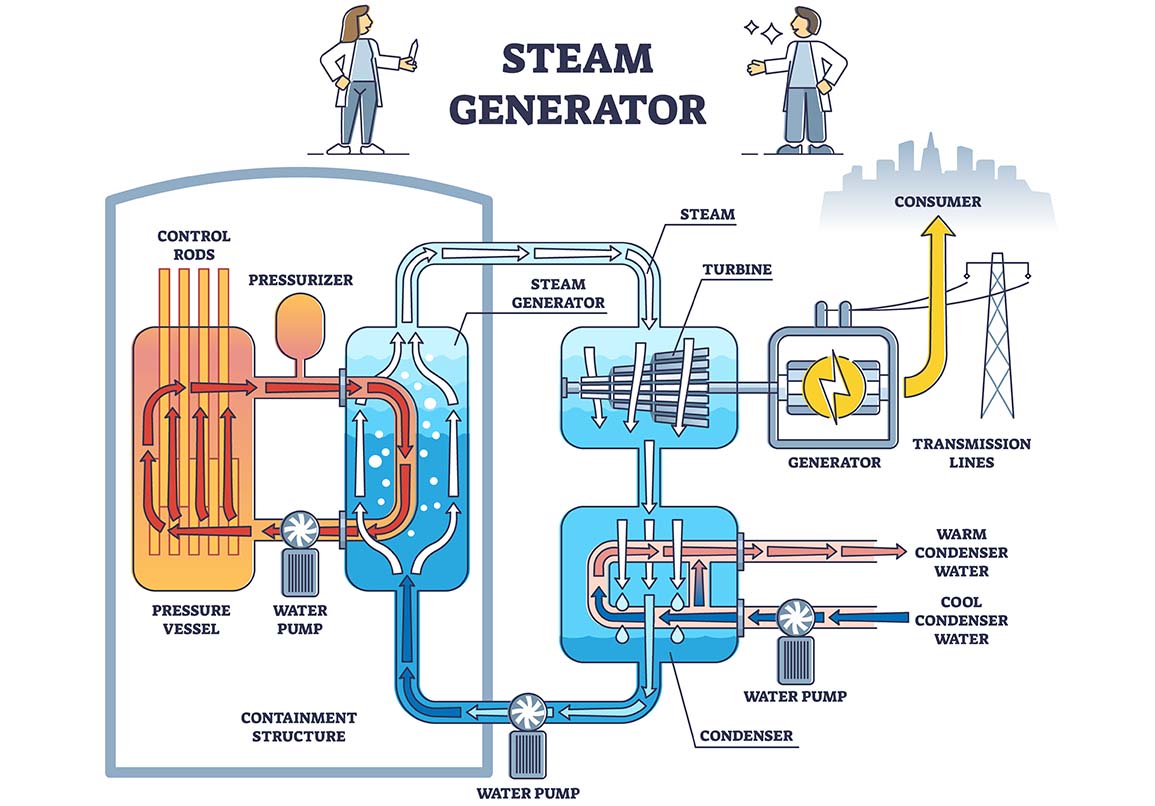
- Thermal - in thermal power plants, energy sources like gas or nuclear, release their stored energy to boil water. The boiling water produces high-pressure steam, which will drive a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator.
- Mechanical - mechanical power plants are very similar to thermal power plants. The difference is that they use different energy sources to drive an electrical generator. Wind farms are great examples of mechanical power plants where wind energy turns wind turbines to generate electricity.
- Other - other power plants use different power sources like photovoltaic or hydrogen. These power plants generate energy using chemical and physical reactions.
What is the U.S percentage of electricity generation by energy source?
Since renewable energy sources are relatively new technologies, most energy generated in the U.S. comes from fossil fuels burned in conventional thermal power plants. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, more than one-third of the nation's electricity is generated by natural gas, while fossil fuels stand for 60% of all energy generation.
Nuclear power plants cover almost 20% of the energy production mix, and all renewable energy sources cover the remaining 20%.
Wind turbines have the largest share of energy production within renewable energies, at around 9.2%. Hydropower is about 6.3% and solar is 2.8% of the energy mix.
When was electricity discovered and by who?
When was electricity discovered and by who?
One person did not discover electricity. In ancient Greece, people discovered that amber, when rubbed with silk, attracted feathers and other light objects, which is static electricity.
Hundreds of years passed until the year 1600. In 1600, William Gilbert, a scientist to Queen Elizabeth I, invented the term 'electricity'. He was the first person to recognize the connection between magnetism and electricity.
During the 17th and early 18th centuries many scientists were conducting various research on electricity:
- 1752 - Benjamin Franklin discovered that flashes of lightning are electric by flying a kite with a metal tip into a thunderstorm.
- 1780 - Luigi Galvani discovered that a dead frog's leg touched with a knife prompted movement. Later, Alessandro Volta explained this happened because of the electricity created when moisture contacts two different types of metal (fork and plate).
- 1800 - Pile Volta created the first battery using silver and zinc discs placed between cloth soaked with a salt solution. The unit of voltage was named after him.
- 1820 - Hans Christian Oersted discovered a magnetic field that is generated when electricity flows through a wire. This field affects a compass needle.
- 1821 - Michael Faraday discovered that moving a magnet inside a coil of copper wire generates a tiny current. This led to the invention of electric motors.
- 1826 - André Ampère printed his theory about electricity and magnetism. He was the first one to explain the electro-dynamic theory. The unit of electrical current is named after him - Amperes
- 1827 - George Ohm summed up all previous knowledge and published his complete mathematical theory of electricity.
At this point, we can say electricity was fully discovered.
What do we know about electricity now?
A few years later, Thomas Edison created the first DC (for direct current) electricity generator. In the 1880s, his creation was what provided all electricity in New York.
At a similar time, Nikola Tesla developed the AC (for alternating current) electricity generator. When Thomas Edison heard about Tesla's discovery, he started spreading stories that AC electricity was not safe to use. In 1893, Tesla's system was used to run 100,000 electric lights at Chicago's World Fair, and AC was established to be a power supply in the USA.
Thomas Edison

Nikola Tesla

How much is electricity per month?
How much is electricity per month?
The electricity bill consists of a significant portion of all monthly utility expenses.
Energy usage will differ on many factors like:
- Number of house residents
- Size of house
- Type of house heating
- Type of domestic hot water heating
- And many others.
On average electricity bills can be close to one-third of all costs so it is worth seeing how one can lower their electricity usage and so - save money.

What are average utility bills in the US?
In the United States, the utility bills of people renting an apartment will be around $240 per month, whereas a homeowner will spend closer to $400 a month.
Average US home bills:
- Electricity: $120
- Natural gas: $60
- Water: $70
- Trash/recycling: $15
- Internet: $60
Total cost: $325

How much are electricity bills for different home sizes on average?
Depending on house size, your monthly electricity bill can be close to:
- Studio Apartment (1 residents) - $55/month
- One Bedroom (1 resident) - $60/month
- One Bedroom (2 residents) - $66/month
- Two Bedroom (2 residents) - $76/month
- Three Bedroom (3 residents) - $93/month

What is the difference between DC electricity and AC electricity?
What is the difference between AC and DC electricity?
Conductive materials have free electrons that move from one atom to another when a potential difference is applied within them. In relation to the direction of electrons moving in a closed circuit, electric current is mainly divided into two types: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Alternating current and direct current are the two main forms of charge that power our electrical and electronic world. The main differences are shown in the table below.
Alternating Current |
Direct Current |
|
Definition |
Changes its direction at regular intervals | Flows only one direction |
Direction of electron flow |
Bidirectional | Unidirectional |
Production |
Mainly synchronous generators | Batteries, solar cells, fuel cells |
Frequency |
50 or 60 Hz |
Not applicable |
Transforming |
Easily transformed to other current or voltage levels |
Impossible to raise the DC voltage and current without converting it to AC and then back to DC |
Converting |
AC is converted to DC using a rectifier |
DC is converted to AC using an inverter |
Transmission |
Easy to transmit |
Hard to transmit |
Application |
Factories, industries, domestic purposes |
Electronic equipment, specialized applications |
What is electricity?
What is electricity?
Electricity is a form of usable energy that can be used to power up different electronic devices or used to convert other energy forms, such as heat or mechanical energy. Electricity is considered to be a secondary energy source as it is produced from primary energy sources, like fossil fuels, wind or solar energy [see the article “How to generate electricity”]. Electricity is also used to transport energy to greater distances with low energy losses, which cannot be done with mechanical energy or heat.

The scientific approach to electricity
In order to learn the working principles of electricity, we need to understand what an electron is. Electrons are very small (around 53.5 billion times smaller than a grain of cooking salt), negatively charged particles, which make up all of the atoms in the universe. In regards to electricity, the electrons on the outer layer of the atom (so called valence electrons) are especially important. They can in certain cases, detach from the atom structure and move to another atom. The movement of these electrons in an orderly manner is defined as the electric current (electricity). Electric current can be direct (DC) or alternate (AC).
Conductors or insulators?
As was explained above, the electric current needs valence electrons to move. Different materials have different electron mobility. This means that in some materials it is more difficult to make the electrons move.
Materials with very mobile electrons are called conductors (as they can conduct electricity). Most of the conductors are metals such as aluminium, copper, silver or gold. These metals are most commonly used in electrical wiring. Graphite, concrete and lemon juice are also very good conductors. On the other hand, there are materials in which it is very difficult to make the electrons move. These are known as insulators. The best insulators are inter alia: rubber, air, ceramics, plastics, dry wood or glass.
How does the current flow?
In order to make the current flow, we need some circuitry. As was discussed in the previous paragraph, the circuitry needs to be made out of conductors. For industrial use, the most commonly used conductors are aluminium and copper wires. In addition, the circuit (connection) needs to be a closed loop. The most basic electric circuit consists of an electricity source (e.g. battery, electrical generator), conductive wires, and a device to power up household appliances connected to each other. In the example below, the electricity source is a battery, that is connected to the electrical appliance (lightbulb) using conductor wires. When the connection loop is closed, the electrical current runs from the electricity source to the lighbulb powering it up.


